Stress Echocardiogram (STE)
Stress Echocardiogram (STE)
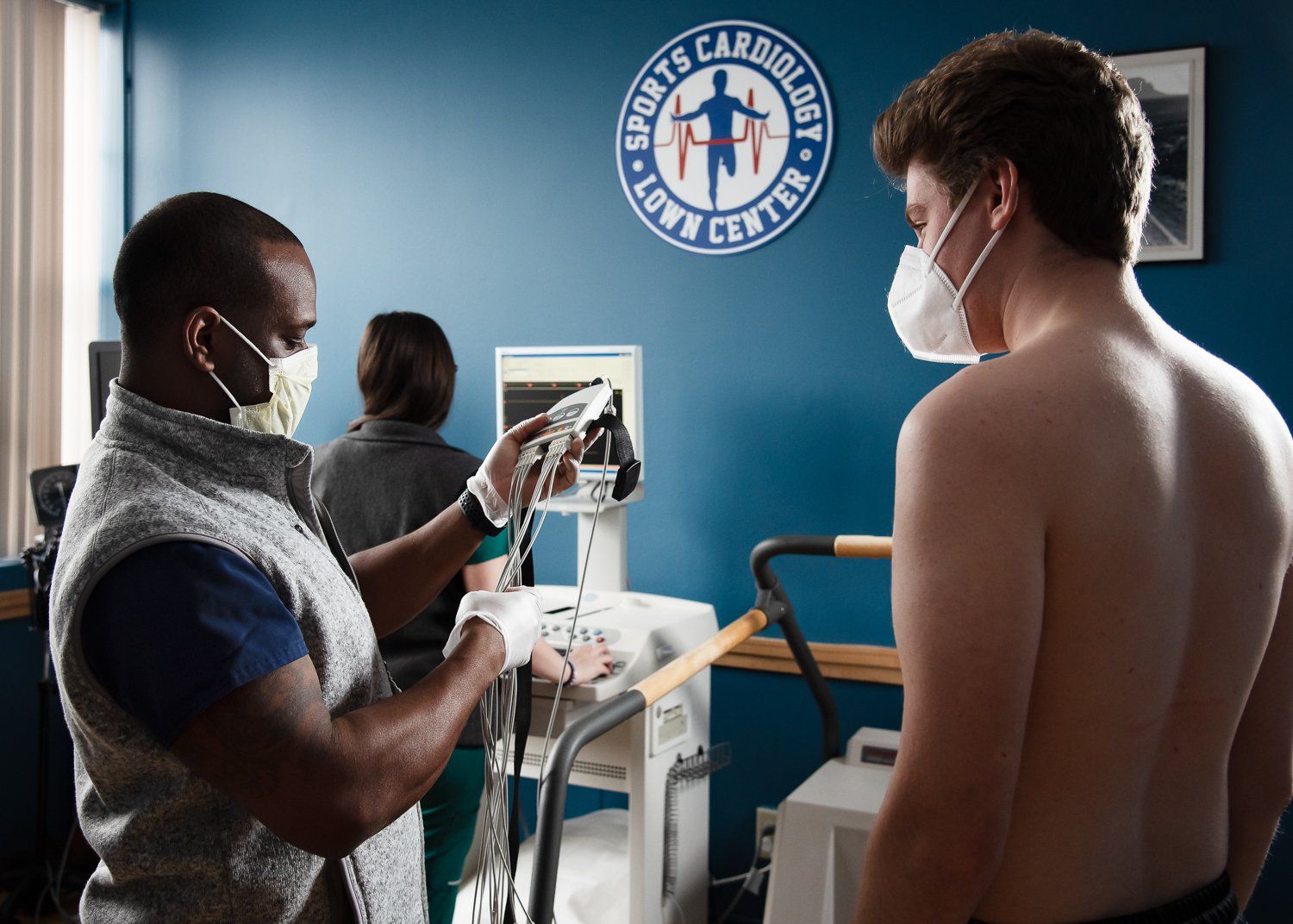
The stress echo combines the exercise tolerance test with an ultrasound of the heart, performed before and after exercise. This test looks at the squeezing function of the heart before and after exercise, which is an indication of blood flow. Your doctor monitors your blood pressure and heart rhythm while you are exercising on a treadmill or a stationary bike and then as your heart rate reaches peak levels, your doctor takes ultrasound mages of your heart to determine whether your heart muscles are getting enough blood and oxygen while you exercise. Normally, the heart function becomes stronger after exercise, however if there are blockages in the heart arteries, the muscle may become weaker.
The test takes approximately one hour from start to finish, including preparation time. Wear (or bring) comfortable clothes and walking shoes. Eat a light meal before the test (do not fast) and take your usual medications unless otherwise directed by your physician. Be sure to drink sufficient water before the test so that you will be well hydrated. A shower and towels are available if you would like to shower afterward.
City skyline
Purpose
Your doctor may order a stress echocardiogram if you have chest pain that they think is due to coronary artery disease or myocardial infarction (heart attack). This test can be administered to clear you for an upcoming surgery or determine how much exercise you can safely tolerate during cardiac rehabilitation.
Other times your doctor may use this test to determine how well heart treatments (such as anti-anginal or antiarrhythmic medications) are working and see if any changes are needed. The test can also evaluate how well other treatments such as bypass grafting or angioplasty are working.